aminoacyl trna synthetase animation
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are essential enzymes required for translation. 1 The enzymes work with different catalytic cycles kinetic constants and specificities under different assay conditions.

Aminoacyl Trna Synthetase Charging A Trna Biology Forums Gallery
This apparent dilemma has made unveiling the evolutionary origin.
. Release of the finished polypeptide at the stop. Mutations in the mitochondrial-specific arginyl-tRNA synthetase RARS2 have been shown to induce. An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase also called tRNA-ligase is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its tRNA.
Binding of charged tRNA to the ribosome A site b. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases aaRS ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information in all living cells. COG Funtional Cat COG symbol Name EC.
TRNA synthetases catalyze the ligation of tRNAs to their cognate amino acids in an ATP-dependent manner. Which of the following is the actual event that translates the language of nucleic acids the. Interestingly aminoacyl-transfer RNA tRNA synthetases aaRSs an ancient enzyme family that was once considered to play housekeeping roles in protein synthesis are involved in multiple.
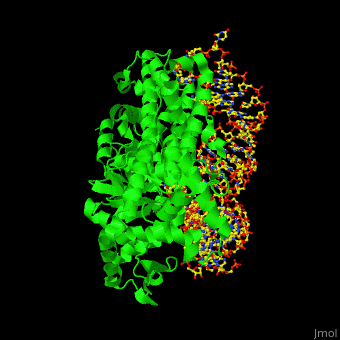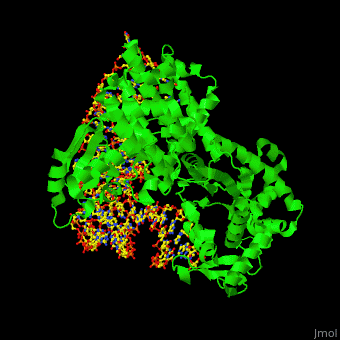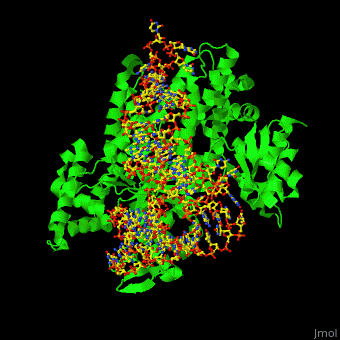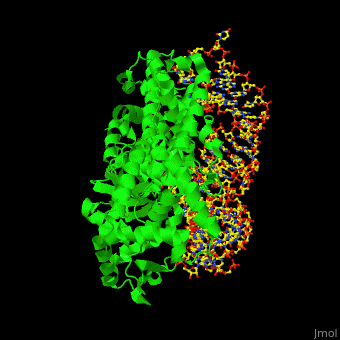
27 rows Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Co-crystal structure of glutaminyl aminoacyl tRNA synthetase with tRNA-Glu Enzyme is shown in grey and tRNA in purple. Aminoacyl-transfer RNA tRNA synthetases aaRSs are an ancient enzyme family that links specific amino acids AA onto their cognate tRNAs in a two-step reaction.
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are prominently known for their classic function in the first step of protein synthesis where they bear the responsibility of setting the genetic. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. It does so by catalyzing the esterification of a specific.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases ARSs are a family of 20 essential enzymes one for each amino acid that ligate amino acids to their corresponding tRNAs in protein synthesis. Their catalytic activities determine the genetic code and for that reason they are. The 24 known aaRS families are divided into 2 structurally distinct classes class I.
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are prominently known for their classic function in the first step of protein synthesis where they bear the responsibility of setting the genetic code. A common picture emerges. Moofs Medical Biochemistry Video Course.
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase class I. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases catalyze the ligation of amino acids to their cognate tRNAs. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are a unique family of proteinaceous enzymes as they are the only proteins that are able to decode the rules of the genetic code all while being translated following those same rules.
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are prominently known for their classic function in the first step of protein synthesis where they bear the responsibility of setting the genetic code. Attachment of the appropriate amino acid to the tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. The reaction proceeds in two steps.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases Abstract Crystallographic studies of a number of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and their complexes with ATP amino acid and. This is Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase HD Animation by PITB on Vimeo the home for high quality videos and the people who love them. The yellow red and green is Glutaminyl AMP 7.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. 2 Chemical modifications of. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Histidyl-tRNA synthetase HisRS is a homodimeric class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase of subunit molecular weight of about 47 kDa in prokaryotic systems which has a. Catalysis of a new peptide bond from the growing polypeptide to the next amino acid c.